
How to Safely Test Unknown Software Using Virtualization
Testing new programs can be exciting, but it also carries risks. Unknown apps may contain hidden malware or cause unwanted system changes. That’s why using virtualization to test unknown software is one of the safest modern practices.
It creates an isolated virtual environment where you can run untrusted programs without touching your real files. This temporary virtual machine acts like a digital sandbox that protects your system from harm. With built-in Windows tools, anyone can perform secure software testing easily. Whether you’re a developer or casual user, virtualization ensures a reliable safe testing environment for every experiment.
What is Windows Sandbox?
Windows Sandbox is a disposable virtual desktop built into certain versions of Windows 10 and Windows 11. It creates an isolated Windows instance that lets you run untrusted programs without fear. Every sandboxed session is temporary—once you close it, Windows automatically removes all changes and resets to its default clean state.
This sandbox mode in Windows works by leveraging virtualization support already present in your hardware. It allows the OS to emulate a fresh temporary Windows environment, helping you install unknown apps or test browser extensions safely. According to Microsoft Docs, the Sandbox runs independently from your main PC, ensuring full system protection during testing.
Key Features of Windows Sandbox
Windows Sandbox is not just fast—it’s intelligent. Once activated, it loads a clean isolated virtual environment using minimal system resources. This makes it ideal for secure software testing.
Each sandbox configuration deletes itself after use, saving you from manual cleanup. It supports malware isolation, automatic file disposal, and integrates tightly with Windows security tools. You can install trial software safely, test scripts, or inspect installers while ensuring your data remains untouched.
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Isolation | Creates a secure, separate environment for apps |
| Temporary Nature | Deletes all data when closed |
| Performance | Lightweight with low CPU/RAM impact |
| Integration | Uses existing Windows Features settings |
Common Use Cases for Windows Sandbox
This feature is designed for everyday users, developers, and cybersecurity professionals. You can use it to test unknown applications, install trial software safely, or open potentially harmful attachments.
IT administrators often rely on it to run untrusted programs and monitor their behavior without affecting the host operating system. It’s equally useful for tech bloggers or researchers who need safe app testing on Windows environment before reviewing software publicly.
Related Guides
How to Enable and Use Windows Sandbox
To begin, open the Control Panel and navigate to Programs and Features, then click Turn Windows features on or off. You can also open the optionalfeatures command from the Start menu. Scroll down and check Windows Sandbox, then click OK.
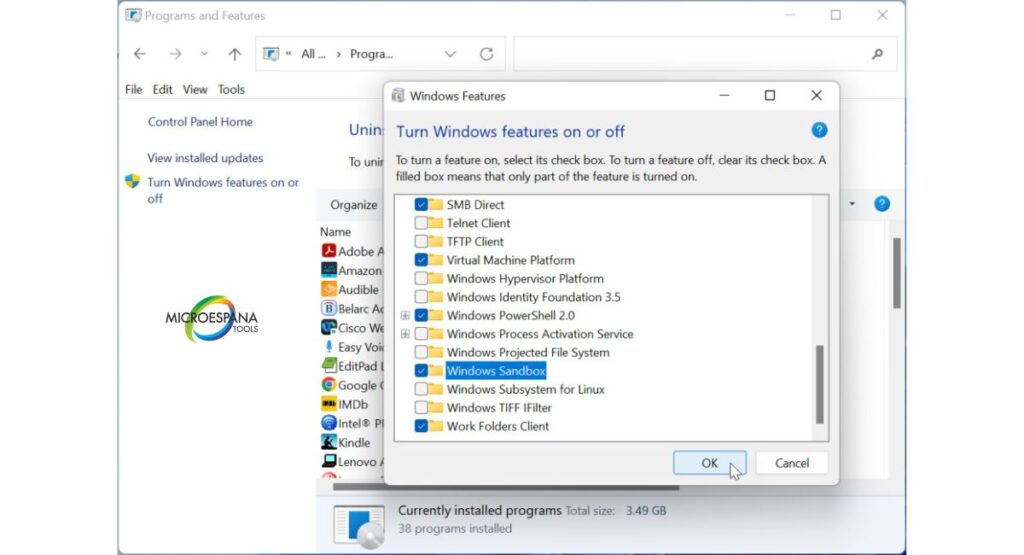
Figure 1: Windows Features Dialog
Alternatively, use the PowerShell command line:
Run as Administrator:
Enable-WindowsOptionalFeature -FeatureName "Containers-DisposableClientVM" -All -Online
Run this PowerShell command for Sandbox as administrator, then reboot system. Once enabled, launch it from the Start menu.
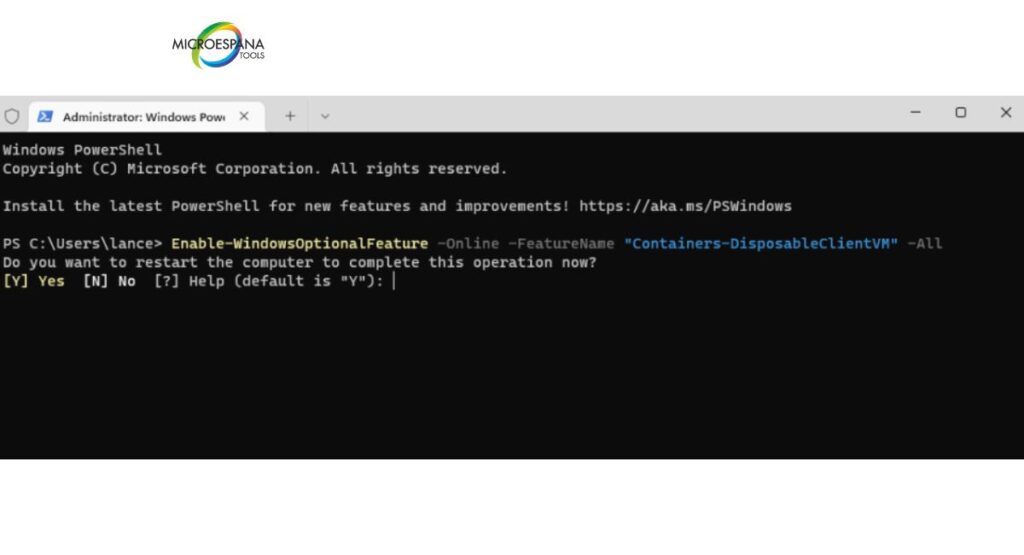
Figure 2: The Isolated Sandbox Environment
Setting Up Windows Sandbox on Windows 11
Windows 11 offers even smoother virtual machine setup. To use it, ensure virtualization is enabled in your BIOS. Restart your computer and press the key shown on screen (usually F2, F10, or DEL). Then, locate “Virtualization Technology” and enable virtualization in BIOS.
After setup, open the Sandbox and drag any app or file you want to test into this temporary virtual machine. It launches in seconds, allowing instant safe testing environment creation.
Using Run-in-Sandbox for Enhanced Usability
The “Run in Sandbox” function lets you automate app testing without manually opening the Sandbox window. It’s perfect for repetitive tasks like checking multiple installers or scripts.
Through the PowerShell command for Sandbox, you can create custom configurations to test different apps safely. Developers love this because they can observe code behavior in a disposable virtual desktop while keeping the base system secure.
Windows Sandbox Makes Testing Programs Safer
Running software in Sandbox means you’re working in a temporary Windows environment that isolates every action. Even if the program is malicious, it can’t harm your main OS. Once you close it, all traces vanish automatically.
In one case study from ZDNet, a researcher tested dozens of suspicious EXE files. None of the malware samples escaped the isolated Windows instance, proving its reliability as a safe testing environment.
Troubleshooting Problems in a Sandbox
Sometimes Sandbox may fail to start or load properly. If you see a “virtualization not enabled” error, open Task Manager, switch to the performance tab, and confirm that virtualization enabled is visible.
If issues persist, recheck Windows Features settings or rerun the Enable-WindowsOptionalFeature command. Occasionally, updates to Windows Defender or driver conflicts can block Sandbox. Restart and retry after system updates to restore stability.
Alternatives to Windows Sandbox for Windows 11 Home
Windows Sandbox is available only on Windows Professional and Enterprise editions, but Home users have other options. Tools like VirtualBox, VMware Workstation Player, or Sandboxie allow you to create a temporary virtual machine with similar protection.
| Tool | Cost | Ease of Use | Isolation Level |
|---|---|---|---|
| VirtualBox | Free | Moderate | High |
| VMware Player | Free | Easy | High |
| Sandboxie | Free | Very Easy | Medium |
Each option provides malware isolation and safe virtual machine setup, ensuring your PC remains safe from bad code.
Limitations of Windows Sandbox
Despite its brilliance, the Sandbox has a few limits. It only works on Windows Professional and Enterprise editions, not Home versions. It also doesn’t save installed apps or files after closing—it’s meant for temporary Windows environments only.
Advanced users may find customization limited, as you can’t change hardware resources extensively or retain system states between sessions. Still, its safe testing environment and simplicity make it an essential Windows security tool.
How Else Can You Test Applications?
There are many other ways to test unknown applications. You can create a full virtual machine setup with Hyper-V, VMware, or use cloud-based sandboxes like Any.Run. These allow more control, snapshots, and persistent storage.
Another modern approach is containerization using Docker, though it’s more complex. It’s excellent for developers needing repeatable isolated environments. In all cases, the goal is secure software testing without risking your main OS.
System Requirements for Windows Sandbox
To enable Windows Sandbox feature, you’ll need Windows 10/11 Pro or Enterprise, 64-bit processor, and at least 4 GB of RAM (8 GB recommended). Your CPU must support virtualization support.
To verify, open Task Manager, check the performance tab, and ensure “virtualization enabled” appears. You can also open the Control Panel, navigate to Programs and Features, and verify the Sandbox component under Windows Features settings.
Best Practices for Safely Testing Unknown Software
Always use updated Windows security tools before testing. Scan any file with antivirus first. Never log into personal accounts in your Sandbox. Avoid storing sensitive files or credentials.
If you use full virtual machines, take snapshots before installing anything. When finished, roll back to a clean state. This keeps your safe testing environment uncompromised and ready for the next secure software testing session.
Conclusion
Learning how to safely test unknown software using virtualization gives you confidence to explore new tools freely. With Windows Sandbox, virtual machine setup, and proper sandbox configuration, you can try untrusted programs, explore new apps, and protect your host operating system effortlessly.

